PCAP and AR Touchscreens in a Rugged Environment
Updated: December, 2024
Summary
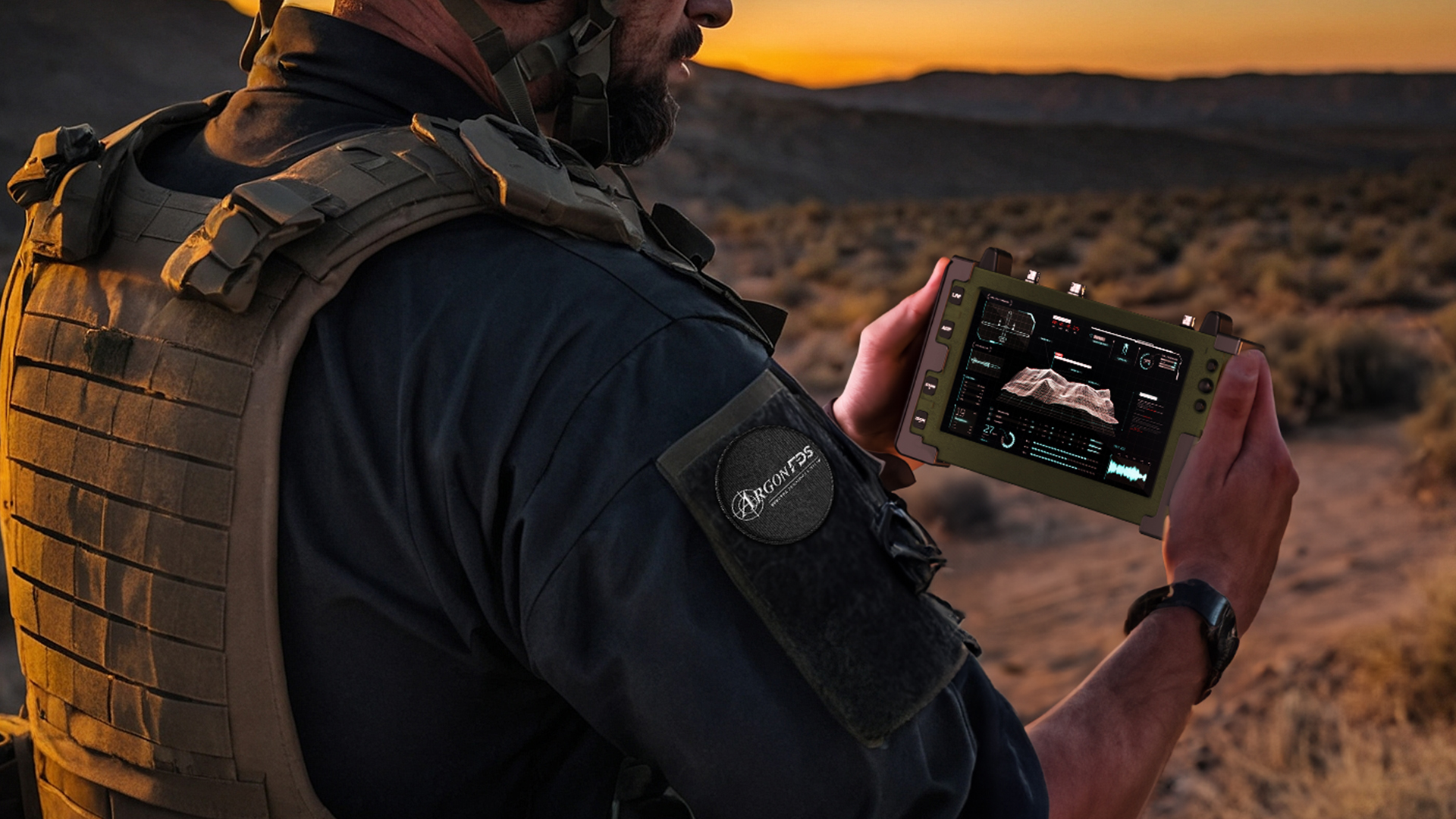
This document reviews the differences and similarities between a Projected Capacitive touchscreen (PCAP) and an Analog Resistive touchscreen (AR) for rugged environment applications. The two can be summarized by noting that PCAP touch works with electrical capacitance (familiar to smartphone users) whereas AR touch works with the application of pressure.
Technology Overview
Projected Capacitive (PCAP): PCAP touchscreens use a transparent conductive coating of sensors. When a capacitive body (finger or stylus) contacts the surface, the sensors detect the conductive properties and register a touch event.
Analog Resistive (AR): AR touchscreens have two transparent layers separated by a thin gap. Each layer’s internal surface features a conductive coating. Touch events are recorded when the two layers are pressed against each other, allowing voltage to pass through.
Technical Comparison
Multi-touch Capabilities
- PCAP: Supports up to 10 simultaneous touches and gestures such as pinch, scroll, rotation, zoom and flip. This provides excellent responsivity for multi-touch
- AR: Typically limited to single touch, with some models supporting multi-touch
Environmental performance
- Durability
- PCAP: Features chemically strengthened glass (Gorilla Glass) with 9H pencil hardness for superior scratch resistance allowing for continued use even after being cracked or damaged
- AR: Plastic upper sensor layer with optional glass protection layer for additional ruggedness
- Display Characteristics
- PCAP: Superior sunlight readability
- AR: Multiple layers can result in reduced light output due to reflectance on surface; susceptible to yellowing or hazing over time
- Input Methods
- Both technologies work with fingers, gloves or stylus and perform well in dusty, humid or moist conditions.
- PCAP: Requires capacitive-compatible input devices; calibration needed for varying input sizes
- AR: Works with pressure input from finger, glove or stylus
Electro-Magnetic Conditions
- PCAP: Requires specific EMI protection; can meet MIL-STD-461F standard for radiated emissions and electromagnetic compatibility and MIL-STE-1275E for electrostatic discharge
- AR: Inherently resistant to electromagnetic interference
Cost Considerations
PCAP and AR touchscreens are similar in cost.
| PCAP touchscreen | AR touchscreen | |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Touch | Great - Up to 10 | Good - Up to 2 |
| Touch detection | Good – requires capacitive object | Great – any object |
| Toughness | Great - Up to 9H hardness | Good – Up to 7H hardness |
| Optical Transmissivity | Great | Good – can degrade over time |
| Water/Dust/Humidity | Good – can be calibrated for best (Great) performance | Great |
| EMI | Great | Great |
Below: qualification tests that have been performed and qualified on ArgonFDS display products with PCAP and AR touchscreens.
| EMI Qualification RTCA DO-160F | Electrical MIL-STD-461G | Environmental Qualification RTCA DO-160F |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Effect | RE102 | Altitude |
| Inrush Current | RS103 | Decompression |
| Voltage Spike | CS 101, Audio Freq CS | Overpressure |
| Induced Signal Susceptibility | CS114 | Ground Survival High Temperature |
| Emission of RF Energy, Radiated | CS115 | Operating High Temperature |
| Emission of RF Energy, Conducted | CS116 | Operating Low Temperature |
| Lightning Induced Transient Susceptibility | CS118 | Ground Survival Low Temperature |
| RE102 | CE102 | Short Time Operating Low Temperature |
| RS103 | Short Time Operating High Temperature | |
| CS 101, Audio Freq CS | Temperature Shock | |
| CS114 | Sand and Dust | |
| CS115 | Fungus Resistance | |
| CS116 | Waterproofness | |
| CS118 | Fluid Susceptibility | |
| CE102 | Humidity | |
| Flammability | ||
| Vibration (Functional) | ||
| Shock and Operational Safety |
Conclusion
Choosing between PCAP and AR technologies should be based on specific application requirements, particularly:
- Input method requirements
- Environmental conditions
- Display clarity needs
- EMI protection requirements
- Expected service life
Each technology offers distinct advantages in rugged environments, making the final selection dependent on specific use-case priorities.
Have questions? Let’s connect!